September 27, 2024 – Calcium Carbonate: A Versatile Raw Material with Diverse Crystal Morphologies Catering to Various Industries
Calcium carbonate, a vital raw material in the chemical industry, boasts a wide array of crystal morphologies, including cubic, spindle-shaped, chain-like, spherical, flake-like, and needle-like forms. Each unique morphology plays a distinctive role in specific industries.
In the ink production sector, cubic or spherical calcium carbonate is highly favored due to its exceptional dispersion and stability. Conversely, the rubber industry prefers needle-like or chain-like calcium carbonate to enhance the mechanical properties of materials. Ceramic manufacturing, on the other hand, demands high-purity, micro-fine spherical calcium carbonate, adhering to stringent requirements. To meet these diverse needs, the chemical industry has adopted advanced crystal morphology control technology, successfully producing various crystal forms of calcium carbonate products through precise regulation of the crystallization process.

According to AsiaMB, temperature control is crucial in the preparation of cubic calcium carbonate. When the crystal formation temperature is below 30℃, cubic calcium carbonate can be obtained through carbonation reaction without the addition of extra crystal morphology control agents. This discovery provides a more economical and efficient method for industrial production.
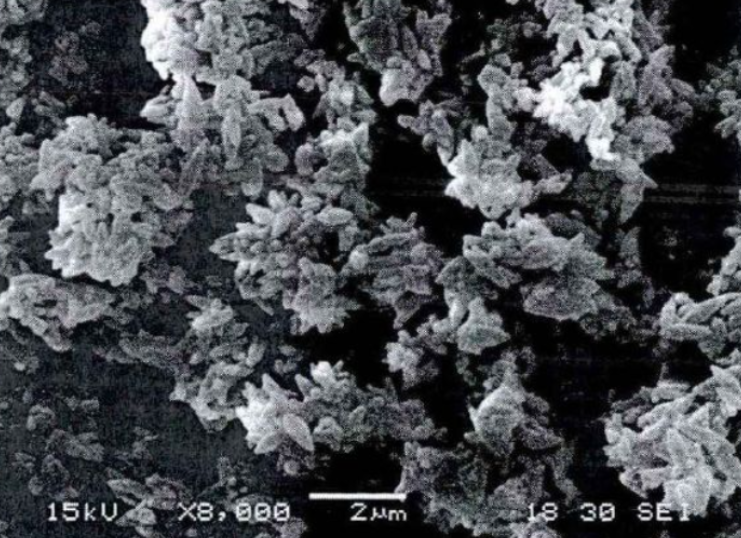
Rose-shaped and spindle-shaped calcium carbonate find extensive applications in industries such as papermaking, rubber, plastics, and coatings. In particular, the addition of spindle-shaped calcium carbonate in high-grade cigarette paper significantly improves the paper’s combustion and breathability. Shiroishi Kogyo Co., Ltd. in Japan has set a new benchmark in the industry by successfully preparing spindle-shaped calcium carbonate with a particle size of 0.1-1.0μm through the combination of wet grinding and carbonation technology.
Chain-like calcium carbonate, with its unique structure and good dispersion, excels in rubber and plastic matrix materials. Its breaking points have high activity and can tightly bond with the matrix material, thereby greatly enhancing the physical properties of the material. The synthesis of chain-like calcium carbonate typically requires the addition of specific crystal morphology control agents during the carbonation process to control the growth of crystal nuclei.
Spherical calcium carbonate, known for its excellent smoothness, flowability, and dispersion, has found wide applications in multiple fields. Various preparation methods include adding hydrogen peroxide to a calcium hydroxide suspension at low temperatures followed by a carbonation reaction, or using sodium silicate as a crystal morphology control additive in the lime carbonation process. A US patent has also reported a four-stage carbonation method for preparing spherical calcium carbonate, further enriching the preparation techniques for this morphology.
Flake-like calcium carbonate exhibits outstanding ink absorption, whiteness, printability, and smoothness in the papermaking industry. Its unconventional arrangement赋予 mixtures higher smoothness, gloss, electrical resistivity, and elastic modulus. When used as a coating pigment for art paper, the flowability and dispersion of flake-like calcium carbonate are particularly prominent.
Needle-like calcium carbonate, with its significant aspect ratio, plays a crucial reinforcing role in the plastics and rubber industries. A research team from East China University of Science and Technology has successfully prepared needle-like nano-calcium carbonate with a narrow particle size distribution and good dispersion by precisely controlling reaction conditions, providing a new option for the industry.
In conclusion, the diverse crystal morphologies of calcium carbonate offer a rich selection of raw materials for the chemical industry, meeting the specific demands of different industries for calcium carbonate products. With the continuous development of crystal morphology control technology, it is believed that the application fields of calcium carbonate will become even more extensive in the future.














